Glenn E. Fleming, MD, MPH, Contributor, MarketHive
(Reposted from Patrick Sexton, https://varvy.com)
Definition:
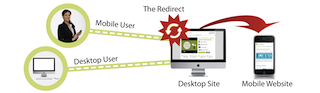
- A redirect is a method of forwarding a user from one web address to another web address. Under normal conditions, when a mobile device requests a certain document at a certain address, the server will normally just provide that document. There are four common types of redirects which will be covered over the course of this series. They include: Initial redirect (canonical), secure pages redirect (SSL), redirect to mobile, and content-driven redirects.

When there is a redirect, the web server does not provide the document. Instead, it provides a new address for the document. The mobile device receives the address and makes a new request for the document to the new address. Then and only then does it receive the document.
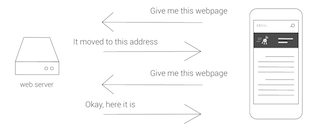
Why is this important? Most importantly, the process can significantly decrease the performance of the website in question. More specifically, a redirect can cause a mobile network to operate very slowly because each time any communication happens between the device and the web server, many things have to happen to facilitate that communication.
Redirects are very slow on mobile devices and should be avoided. If they have to happen, the amount of redirects should be as few as possible.
Redirects can be quite costly on mobile networks. Typically, with very redirect removed from your website, there will be a significant improvement in the speed in which your content is seen by users.
David